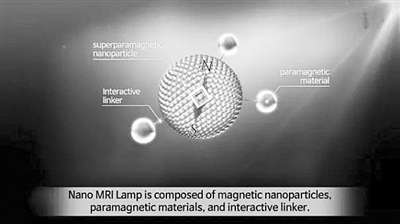
New technology for genetic testing New concept contrast agent "nano MRI lamp" Brazilian genetically modified soybean Recording DNA data Membrane material with stealth effect (simulation effect diagram) Water resistant ultra-thin solar cell Biomedical Science United States Gene editing technology, hot stem cell research breakthrough Although security was once questioned, the development of genetic editing technology is unstoppable. The US scientists conducted the first genetic editing study of human embryos in the country and conducted the world's first human genome editing experiment. Not only did they validate the safety of gene-editing human early embryonic DNA, but they also showed that gene editing technology can edit crop genes and increase crop yields. The patent dispute between the Bode Institute and the University of California at Berkeley has finally settled, but technical competition continues: the former developed a new CRISPR diagnostic system and a new base editor, the latter found Mechanisms to reduce off-target effects of CRISPR technology. Significant progress has been made in stem cell research. Scientists have discovered that embryonic stem cells are similar to the developmental potential of fertilized eggs, produce cells with hematopoietic stem cell function, and successfully use antibodies to program adult cells into pluripotent stem cells. The 3D image collection of different stem cells of the same mother cell under the name "Allen Stem Cell Browser" is published online, which strongly promotes the study of cell structure changes related to diseases such as cancer. Research on a variety of human diseases has been carried out extensively, especially in the research of AIDS, Ebola, and Zika, and many other major achievements have been made, which have attracted attention and laid a solid foundation for human beings to finally overcome these diseases. United Kingdom "Three Parents" Baby Technology Approved Continued Funding for Biological Science Research Zheng Huanbin (Reporter in the UK) The British Bureau of Artificial Insemination and Embryology announced in March that it has approved the first application for the use of nuclear-transplanted “three-parent†infant technology to make this controversial technology a useful application in fertility treatment. A substantial step. In March, the British Biobank also announced that it will genetically sequence a sample of 500,000 volunteer participants owned by the bank, which is expected to cost £150 million for three to five years. In research, the UK Biotechnology and Bioscience Research Council announced that the government will continue to invest 319 million pounds to support bioscience research to ensure international competitiveness and address global challenges such as population growth, fossil energy substitution and aging. In September, the Francis Crick Institute of the United Kingdom announced that it has demonstrated the mechanism of action of a key gene in the early developmental stage of human embryos through gene editing technology, which helps scientists to solve some unsolved mysteries of embryonic development and improve in vitro fertilization. And other reproductive assistive technologies. Germany Genetic testing to determine the process of cancer DNA methylation Gu Gang (Reporter in Germany) The Max-Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in Germany collaborated with the Charlotte Hospital in Berlin to develop a new genetic testing technology using simple biomarkers for early detection of rectal cancer tumor biomarkers. It can accurately determine the stage of cancer and decide whether or not to use chemotherapy. Researchers at the Leibniz Institute on Human Aging have for the first time confirmed that when a gene is lost in the promoter of a gene, the gene will go wrong. The result is an abnormal protein that interferes with the composition of normal cells, causing massive disruption of cell function and identity, cell variability and possibly cancer, which is a mysterious process of DNA methylation. Wu Jianqiang, research group of Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, cooperated with Max Planck Institute of Chemical Ecology to discover that the parasitic herb called the dodder has the ability to transmit insect-resistant signals among host plants, and provides new enlightenment for the harm of parasitic plants in agriculture. . Russia Specific disease research results in artificial blood through Phase I clinical Yan Kewei (Reporter in Russia) In 2017, the Russian Academy of Sciences systematic research institutions have achieved a number of new achievements in the medical field: plans to use stem cells to treat varicose veins; trial production of nanogel particles that can control skin cancer; For bioassay of drug detection, this technology has been adopted by the Bayer Group of Germany; it has been found to delay the aging of tissues by restoring normal work of mitochondria with the help of melatonin. In the fight against AIDS, scientists at the Genomics Bioinformatics Center of St. Petersburg University plan to find effective ways to treat AIDS by studying the innate immunity of some Europeans to HIV; scientists from Russia and China announced that they will jointly develop a combination vaccine for AIDS. The vaccine includes the DNA component of Russia (DNA vaccine) and the accelerating protein (enhancer protein) component of China. Artificial blood technology has become a new direction in Russian biotechnology. The Ikalu California hemoglobin-based blood substitute project has passed the first phase of human clinical trials, which are expected to be an effective way to address blood shortages in the event of war, terrorist attacks, and natural disasters. The Russian Ministry of Defense's General Administration of Research Activities announced that the Russian Ministry of Defense is testing a new type of military artificial blood that is more oxygen-carrying than similar products. Korea The achievements of biotechnology are often reshaped Qiju (Reporter in South Korea) Biotechnology is the core content of the science and technology development policies of successive Korean governments, and it is tilted from various aspects such as funds and policies. South Korea has achieved a lot of results in the field of biotechnology and is reshaping its academic reputation. Seoul National University has developed a new method that does not use induced differentiation technology to improve the safety of stem cell therapy, and can differentiate mesodermal adipose-derived stem cells into neural stem cells of different systems. The Korean and American research groups have successfully repaired a genetic variant in the embryo that can induce hypertrophic cardiomyopathy using gene editing technology. Using this technique to cut off the mutated gene, the normal gene is repaired intracellularly. South Korea has successfully developed a new concept contrast agent "nano MRI lamp", which can greatly improve the difference between diseased tissues and surrounding tissues, and can replace pathological examination for cancer diagnosis and other analysis and examination. Seoul National University and Gangwon University have successfully produced artificial livers for human transplantation. Japan Progress in research on genetic diseases of drought-resistant rice breeding Chen Chao (Reporter in Japan) The Japanese Institute of Physical Chemistry announced in April that they have planted the Arabidopsis galactosidase synthase gene (AtGolS2) into the currently popular rice variety and successfully developed drought-tolerant transgenes. Rice. Great progress has been made in research on genetic diseases. Japanese scientists have found numerous disease models from knockout mice, helping to find the cause of genetic diseases and developing new treatments. In July, the Japanese Institute of Physical Chemistry discovered that 360 knockout mouse strains can be used as model mice for known hereditary rare diseases, and 135 strains can be used as candidates for the new Mendelian genetic disease model. The results of this research place high hopes for scientists to advance the study of unexplained diseases. Bass The genome project results in a significant share of the biopharmaceutical market Deng Guoqing (Reporter in Brazil) The Brazilian government has always attached importance to the development of the bio-industry. The bio-industry plays an important role in the field of national innovation strategy in Brazil and is one of the priority areas for development. Brazilian biotechnology is mainly used in agriculture, medicine and energy, and research on stem cells, genes, plant organisms and vaccines is a world leader. At present, Brazil has become one of the more developed countries in the global biotechnology industry. Brazil attaches great importance to biotechnology and vigorously implements the genome project. The world ranking in deciphering and mapping the genome map of human cancer cells is second only to the United States. According to data released by the Brazilian Biotechnology Industry Association, the main achievements of Brazilian biotechnology include: the world's leading data for the international human genetic database; the leading research on genetics for citrus and sugarcane diseases; cotton in the field of transgenic technology such as cotton The insect resistance, the antiviral properties of cowpea, and the herbicide-free herbicide research are obvious; the development of vaccine against tropical diseases is synchronized with the world level. A new genetically modified soybean variety was approved, which contained two insect-resistant genes and was tolerant to three herbicides, glyphosate, glufosinate and dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Brazil has the largest biopharmaceutical market in Latin America. It is predicted that in 2017, the Brazilian pharmaceutical market share will exceed 40 billion US dollars, or become the world's fourth largest pharmaceutical market. Ukraine Medical materials are endlessly biocompatible into bright spots Zhang Hao (Reporter in Ukraine) The Institute of Materials Science of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine has developed a new titanium-based (Ti-Si-Nb) biocompatible alloy characterized by low modulus of elasticity and non-toxicity to the human body. More than 5% to 20% of metal materials widely used in the medical field, the compatibility with bone materials can be optimized. The Institute of Physics of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine produces a radiation cross-linked hydrogel medical dressing for the treatment of burns and wound healing. The hydrogel flexible film has a thickness of 3-4 mm and is a sterile transparent gel-like material with a moisture content of 80%-90%. It is biocompatible and helps to seal, cool and heal the wound. Israel Using Cloud Software to Analyze Crop Artificial Seawater and Innovate Aquaculture Mao Li (Reporter in Israel) Geneformics' technology can provide lossless data compression technology for large individual genomic data, save space in the genomic database, and support future potential genomic data storage needs. The startup NRGene mapped the genomes of bread wheat, pasta wheat and wild-type gluten wheat, and collaborated with Chinese genomics technology company Keno to explore the genetic composition of upland cotton. In addition, the company plans to use its genome sequencing software and algorithms to authorize the analysis of human DNA, to help diagnose early genetic diseases, and to provide personalized drug treatment for patients. NRGene has reached an agreement with Monsanto and Illumina, a genomic research and technology development company, to jointly build a cloud software for genomic analysis, and to strengthen Monsanto's prediction, comparison and selection of the best genetic components from massive genetic, genomic and trait information. The company's cloud-based software helps customers quickly and efficiently research the genome of crops and make better assessments of crop traits to improve agricultural productivity. The technology developed by Latimeria can produce artificial seawater and carry out marine (such as salmon) farming, which reduces the dependence on seawater and saves water while improving the cleanliness of aquaculture water. new material United States The heat of two-dimensional materials is not reduced by the results of flexible materials. Liu Haiying (Reporter in the United States) In 2017, graphene is still the focus of two-dimensional materials research. Not only have scientists developed porous 3D graphene structures that are small but very strong, but they have also developed graphene permeable membranes that penetrate more than 10 times faster than current systems. These results have opened up broader prospects for graphene applications. The layered 2D structure electron crystals with better conductivity than graphene, 2D magnets made of chromium triiodide, and micro-devices made of molybdenum disulfide that can pull more than 100 times their weight are fully displayed. The potential of two-dimensional materials to change the world. Flexible materials and lightweight materials are also the focus of research and development in the field of new materials: flexible light-absorbing materials with stealth performance, which can increase the efficiency of solar cells by more than 3 times; ultra-light crystalline aluminum with a density of only 0.61 g/cm3; liquid at room temperature Metal alloys can be used to make flexible transistors. American and Austrian scientists have jointly developed a new material - the outer - Kondo semi-metal, a material that can be used in quantum computers, with some properties that cannot be explained by classical physics but only by quantum mechanics. It is also worth mentioning that Harvard University announced in January that it produced the first metal hydrogen on the earth, causing a sensation, but a month later, this metal hydrogen sample disappeared due to experimental operation errors. This has become a major regret in the field of new materials research in 2017. Japan Rubber solar cell made of extremely strong material can be washed Chen Chao (Reporter in Japan) Hokkaido University has successfully developed a high-strength "fiber-reinforced gel" by combining hydrogel with fiberglass textiles. It is easy to bend, tough and super-metal, and can be made into a tough fiber-reinforced rubber by compounding with rubber. The washable paste type power supply is expected to be realized. The organic solar cells developed by the Institute of Physical Chemistry of Japan and the University of Tokyo are not only ultra-thin, but have an energy conversion rate of 7.9% and extremely high water resistance. For the first time, the University of Tokyo and the Institute of Physical Chemistry discovered "Well particles" in the magnetic body (Mn3Sn). So far, humans have discovered a new magnetic body "Well magnet" which is different from ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic. Weir magnets can generate huge Hall voltages even in the absence of a magnetic field, and have the unique material properties of the new quantum function, opening a new path for the realization of Will particle driven quantum computers. The new energy industry technology comprehensive development organization successfully synthesized high-purity FeNi superlattice magnet materials for the first time in the world. The new synthesis method is simple in process and suitable for industrial production, and will greatly advance the application process of obtaining high-performance magnets without using rare earth elements. Germany Antiferromagnetics into new research sunglasses lenses can be charged Gu Gang (Reporter in Germany) The Ulysse Research Center in Germany collaborated with the National Laboratory of Hefei Microscale Material Science at the University of Science and Technology of China to prepare artificial antiferromagnetics based on the all-oxide epitaxial system. The results, published in the 2017 issue of Science, have been evaluated as a very high-level experimental work, a stunt in sample quality and characterization, opening up a new direction in the study of other oxide multilayer film materials. Researchers at Karlsruhe Institute of Technology invented translucent colored sunglasses that use solar energy to charge mobile phones. The organic solar cells of the lens have a microprocessor and two power displays that show the sun's light intensity and ambient temperature. This technology may also lay the foundation for further application of solar energy, such as embedding organic solar cells into windows or glass skylights. Korea Semiconductor production, the world's leading electronic ink printing circuit é‚° ( (Reporter in South Korea) South Korea has maintained a leading position in the field of semiconductor materials, semiconductor production is still the world's leading ranks, especially memory and other bulk products, of which 50% are sold to the Chinese market. The Korea National Defense Science Research Institute has developed a plasma fabric manufacturing technology that uses "flexible electrodes" to fabricate wearable plasma fabrics of different sizes and shapes, such as anti-chemical, anti-virus, sterilization, medical equipment and other fields. . The research team at Chongshi University in Korea has developed a variety of sensory electronic skins using polymer materials. Its tactile perception is similar to that of animal skin. It also senses air fluctuations and has broad potential in medical, aerospace and other fields. use. The Korea Electric Technology Research Institute has released an electronic ink with carbon nanotubes and nanoparticles added. By controlling the surface tension of the ink, it is possible to print out hundreds of nanometer-scale electrical lines using a 3D printer, greatly increasing the usability of 3D printing technology. Bass Pay attention to the development of nanotechnology and develop new products and processes Deng Guoqing (Reporter of the newspaper in Brazil) At present, the world's annual investment in nanotechnology development is close to 2 billion US dollars. It is estimated that the sales of nanotechnology products market will reach 1 trillion US dollars in the next decade. In order to seize this huge potential market, the Brazilian government attaches great importance to the development of nanotechnology. The Brazilian Ministry of Science and Technology has developed a systematic nanotechnology innovation development strategy, established a joint committee for nanotechnology, and is responsible for the national nanotechnology development planning and management, and established the development direction of nanomaterials and nanobiotechnology. The Brazilian Ministry of Science and Technology and the National Science and Technology Development Council have earmarked funds to focus on the development of new nano-products and processes, focusing on nano-biotechnology, new nanomaterials, nanotechnology for optoelectronics, biosensors, tissue bioengineering, Biodegradable nanoparticles and magnetic nanocrystals for administration. Ukraine Indium selenide brings the revolutionary core of electronics to iron-based alloys Zhang Hao (Reporter in Ukraine) In early 2017, Ukrainian and British scientists published an article in the journal Nature·Nanotechnology, arguing that the practical application of indium selenide may lead to a revolution in nanoelectronics. Nano-scale ultra-thin indium selenide is a new graphene-like semiconductor material with unique properties ranging in thickness from one layer to several tens of layers. The nano film of the semiconductor material is obtained from a large number of ingots of indium selenide layered crystals similar in structure to graphene. Through a joint study by Ukrainian and British scientists, indium selenide layered crystals were successfully stripped to a single layer state. In October 2017, the Institute of Metal Physics of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine announced the development of an iron-based alloy that is both metal and metallic glass. The heating elements manufactured by it are low-temperature products that are bendable and not easily damaged. They can be used to produce transformers and sections. The core components of the flow, heating and magnetic conductors. Russia Advanced materials research and development speed up scientific research and production potential enhancement Yan Kewei (Reporter in Russia) In March 2017, Russian President Vladimir Putin signed the Presidential Decree No. 101 on the Establishment of Advanced Materials Development Center to develop the research and production potential of the Russian Federation of Defense Industry Complex. In terms of concrete results, researchers at Moscow University have developed a new type of polymer composite material that can withstand temperatures up to 450 ° C and has far more strength than aviation aluminum - titanium alloys, which will provide the possibility of building ultralight aircraft and satellites. The Russian Research Foundation announced that Russian scientists have developed a membrane that protects against the smallest particles, including viruses, which have stealth effects and can be used for medical, military, and ultralight applications. The soldier's combat uniforms have good concealment. Scientists at the Russian Far Eastern Federal University have developed a polymer luminescent material that turns ordinary windows into solar panels. This concentrator can take advantage of the scattered light that is common in the environment and convert the concentrated light energy into electrical energy. Biodegradable implants based on bioabsorbable polymers from the Russian Institute of Technology are now in clinical trials. The polymer is completely soluble in the body and forms new bone tissue at the site of implantation. (Technology Daily) Tetanus Shot,Tetanus Vaccine,Hepatitis B Injection,Hep B Vaccine FOSHAN PHARMA CO., LTD. , https://www.fspharmamedicine.com