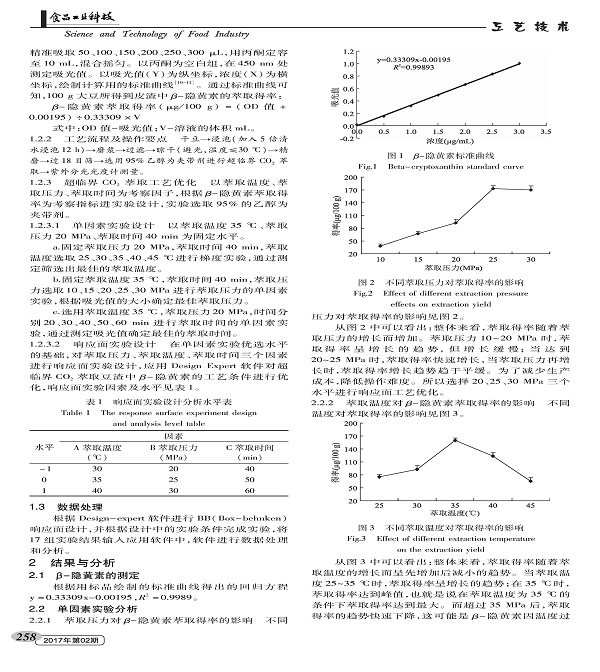
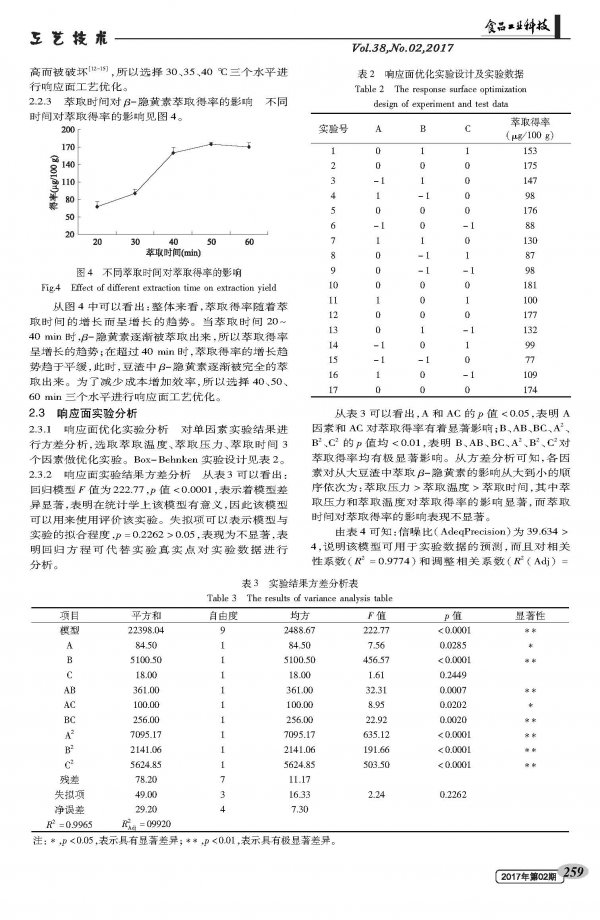
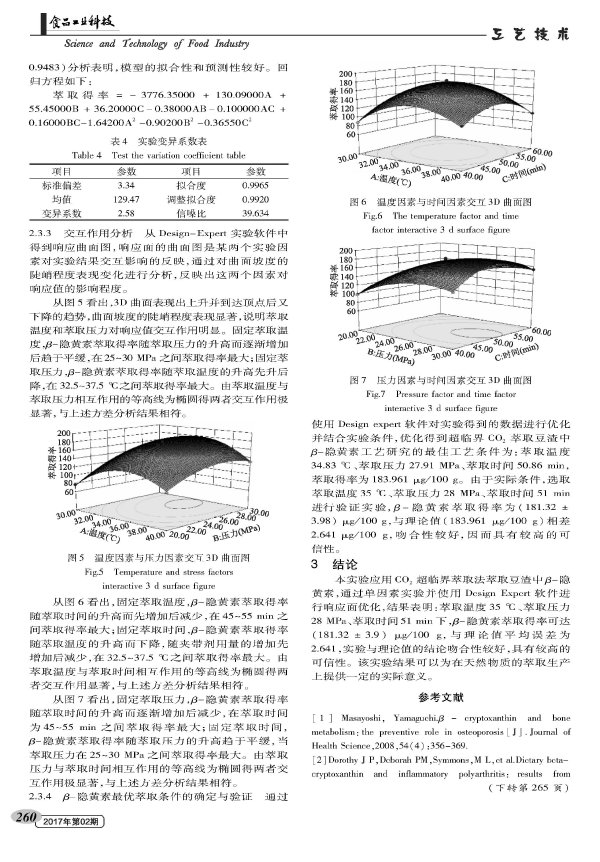
--cryptoxanthin is a natural pigment in carotenoids with a molecular formula of C40H56O and a molecular weight of 552.881. It is one of the essential pigments in human blood. It cannot be synthesized in human body and can only be taken from food. As a precursor of vitamin A, β-cryptoxanthin has the function of protecting eyesight, and has the functions of scavenging free radicals, whitening, promoting skin renewal and repair, anti-fatigue, anti-oxidation, preventing osteoporosis, reducing arthritis risk and lowering blood pressure. Prevent and inhibit a variety of physiological functions such as cancer. Studies have shown that β-cryptoxanthin is present in yellow, orange, red fruits and vegetables and microorganisms. It has been extracted and isolated from papaya, Wenzhou mandarin, pepper, yellow corn, persimmon, pumpkin, physalis and other substances. At present, China is not only the country where soybeans are mainly grown in the world, but also the main soybean processing countries. Bean dregs are by-products of various soybean food processing industries. If we estimate 2t wet bean dregs per 1t of soybeans, we will produce about 10 million tons of wet bean dregs every year. For a long time, bean dregs is a kind of traditional Chinese medicine in all agricultural wastes. Because of the low heat energy and rough taste of bean dregs, it has not attracted enough attention in the past. In addition, because of its large moisture content, easy to spoil and deteriorate, and difficult to transport, it is usually only used as feed or discarded, and has not been well developed and utilized, which greatly wastes the practical application and nutritional value of the bean dregs. The extraction of β-cryptoxanthin from soybean residue is not only the comprehensive development of nutrient components of soybean residue, but also solves the environmental pollution caused by abandoned bean dregs, realizes the recycling of waste, and conforms to the current environmental protection concept and sustainable development strategy.