The ripeness of watermelons is relatively uniform, and the over-concentration of the market makes the market's supply prominently characterized by light-poor. Due to the prosperous season, the price difference between watermelons in the market is very large. The price of the earliest listed and the most recent night market is often 1-3 times higher than the peak market price. Therefore, to do a good job of storage and preservation of watermelons is not only important for regulating market supply and satisfying the needs of consumers, but also can greatly increase the economic income of production, business units and farmers. First, the factors that affect the storage resistance of watermelon. Factors affecting the storage and transportation of watermelon are divided into intrinsic factors and external factors. The internal factors are mainly the maturity, the thickness and hardness of the melon, and the physiological changes inside the melon during storage and transportation. External factors are mainly whether there is mechanical damage, and humidity, temperature, pests, and so on. 1, maturity and melon skin characteristics. Storage of watermelon should choose about 8 mature watermelon, 9 mature or not suitable for long-term storage. The melon skin is thicker, harder, and more flexible and has better resistance to storage and transportation. 2. Physiological changes in melons during storage. It is mainly the change of the sugar content and the hardness of the melon. Changes in the sugar content of watermelons during storage were determined and it was found that the soluble solids content decreased significantly during the first 20 days, from 10.4% to 7.3%, and then gradually decreased. During the storage, the hardness of guava gradually decreased, and the general trend was early and late. 3, mechanical damage. After the watermelon is harvested, it often causes bumps and crushes during handling. Due to differences in size and variety of watermelon, the degree of damage may vary. These injuries are generally difficult to see from the outside, but they can be expressed after short-term storage. For example, the melon skin becomes soft, the skin darkens and darkens, the cells break, the juice overflows, and the flavor deteriorates. 4, the influence of temperature and humidity. During the storage of watermelon, under the premise of not being affected by freezing, lower temperature should be required as much as possible, and it is better to maintain 5-8°C. The higher the temperature, the greater the respiratory depletion, the more intense the ripening process, and the greater the decrease in sugar and quinoa intensity. And the high temperature is conducive to the breeding of fungus and will cause the decay of the watermelon. The requirements for humidity should not be too low, nor too high. Too low a watermelon loses water, the skin becomes soft, and the humidity is high. According to tests, the general humidity is 80%. Second, the main measures to improve the storage and transportation of watermelon 1, choose to store and transport varieties. All the watermelon varieties that are resistant to storage and transportation are mostly hard and flexible, and the changes in sugar content and hardness are relatively slow. For example, Sanchao Jingxin, Almighty Triple Crown, Disease-Resistant King, Super Sweet King Disease-resistant dragons, lazy kings covered the land, disease-resistant nectar, nectar seedless watermelon and so on. 2, suitable maturity. For those who have more than 10 days of production and marketing of watermelons, 75% to 80% of mature harvests; for those with 5-7 days of age, they can harvest at 85% to 90%; for those with 3 days of less than 3 days, they can be 90%. Harvesting; local sales can be harvested at 95% to 10%. 3, reduce mechanical damage. In the process of receiving shipments and sales, we must always take it gently. Minimize all mechanical damage such as impact, pressure, crowding, and stab. 4, the appropriate temperature and humidity. In the process of receiving transportation from the harvest, the temperature and humidity should be kept from being too high or too low. As a long-term storage environment, the temperature of 5-8°C and 80% relative humidity are most suitable, which can effectively prolong the storage time. Third, preparation before storage 1, pre-cooling. The so-called pre-cooling refers to the watermelon body temperature before cooling or cooling to the specified temperature range before transportation or storage, in order to maintain its original quality. The longer the cooling time of watermelon after harvest, the more obvious the quality decline. If the watermelon is not pre-cooled before storage and transport, and the product temperature is high, the respiration will increase in the vehicle or in the warehouse, causing the ambient temperature to continue to rise, and it will soon enter a vicious cycle, which will easily lead to storage failure. The simplest method of precooling is in the field, using nighttime low temperatures to precool overnight and loading or warehousing before the early morning temperatures rise. Where conditions permit, it can also be pre-cooled by mechanical air-cooling method, using fans to circulate cold air, cooling the watermelon by means of heat conduction and latent heat of evaporation, which is generally a tunnel through which the watermelon is blown through a cold wind. The cooling rate of air cooling depends on the product temperature of the watermelon, the flow rate of the air, and the surface area of ​​the watermelon. 2, storage place and watermelon surface disinfection. The watermelon storage place and the disinfection of the surface of the watermelon can use 40% formalin 150-200 times, or 6% copper sulfate or 70% thiophanate-methyl 1000-fold or bleach 0.5-1% solution, or 15- 20% saline solution. Disinfection of the warehouse is even and the containers, baskets, utensils, etc. must be disinfected. Watermelon can be sterilized by immersion, drained after disinfection, put it in the shade and dry it, preferably in combination with pre-cooling. Fourth, storage methods 1, ordinary indoor storage. Choose cool, ventilated, unoccupied free houses for storage. Sweep clean, strictly disinfect, put a layer of wheat straw, sorghum or corn stalks in the house, and then place the watermelon. The watermelon is placed on the yin and yang surface that grows in the field, and the height is preferably 2-3 layers. About 1 meter of sidewalk is left in the house for management inspection. When the temperature is high during the day, doors and windows are closed to reduce the entry of personnel. At night, the temperature is low and the windows are ventilated. The temperature is preferably controlled below 15°C, and the relative humidity is maintained at about 80%. 2, sand law. Fresh watermelon was stored in the vacant room and stored for 45 days. It also maintained good color, aroma, taste and nutritional value. Method: Choose a clean and ventilated house, shop 6-10 cm thick clean fine river sand, harvest 7 ripe watermelons in the sunny evening, 3 watermelon leaves for each watermelon, the ends of the vines cut off from the section 3 cm, cut Immediately stained with ash, leaving 1 green leaf for each melon section. After the melons were shipped back to the house, one by one, they were discharged to the river sand, covered with fine river sand, covered with watermelon 5 cm thick, and 3 leaves revealed nutrients to be produced, and the melons were cooked after being cooked. 3, smear method. The fresh watermelon stalks are ground into a slurry and sprayed with watermelon, and then stored in a common room, can be stored for 85 days, and the good rate can reach 80%. Specific approach: The treated "pharmaceutical" is a fresh watermelon stalk, ground into a slurry, diluted by filtration to 300-500 times liquid, spray wet watermelon surface, and slightly dried, that is, wrap paper (kraft paper, old newspapers) Wrap it in a cool, well-ventilated place and store it in a damp place. During the storage process, pick it up once every 10 days or so and treat the tops of the guars as soft, moldy and rotten. Cardiovascular Drugs refers to Prescription drugs and medicines for diseases relating to the structure and function of the heart and blood vessels. Studies in these areas include: heart failure, coronary artery disease, high cholesterol, blood clots, circulation disorders, and others. A wide range of medications are used to treat various heart conditions. Some examples of the drugs used in cardiovascular medicine include:
Apixban, 99%
Cardiovascular Oral Anticoagulant Medication,Dabigatran Etexilate Mesylate,Blood Thinning Medicine,Blood Thinner Jinan Jianfeng Chemical Co., Ltd. , http://www.pharmachemm.com
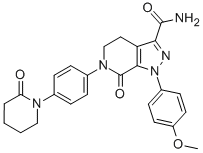
Anticoagulants or blood thinners - These agents prevent coagulation or clotting of the blood. Injectable forms of anticoagulants include dalteparin, enoxaparin, tinzaparin and heparin. Warfarin is a commonly used Blood Thinner that can be taken in the form of a tablet. These drugs do not dissolve existing blood clots but are preventive agents in patients who have had a heart attack.